Dissolution Testing and Rheological Characterization of Medicated Chewing Gums
Dissolution testing of Medicated Chewing Gums
AB FIA offers dissolution testing of medicated chewing gums as an analytical service to clients on a CRO basis (non-GMP). The testing is performed according to European Pharmacopeia 2.9.25, using Apparatus B (the only equipment commercially available). This apparatus is also available for sale from FIA or our distributor Erweka, se products here: https://shop.fia.se/chewing-apparatus/.
For quantification we can use HPLC-based assay methods developed and provided by the client, but we also offer the development of an assay method if this is not available. The analytical test protocol is always planned together with the client but builds on the long-term experience gained within FIA since we launched the equipment in the late 90’s. 1, 2, 3
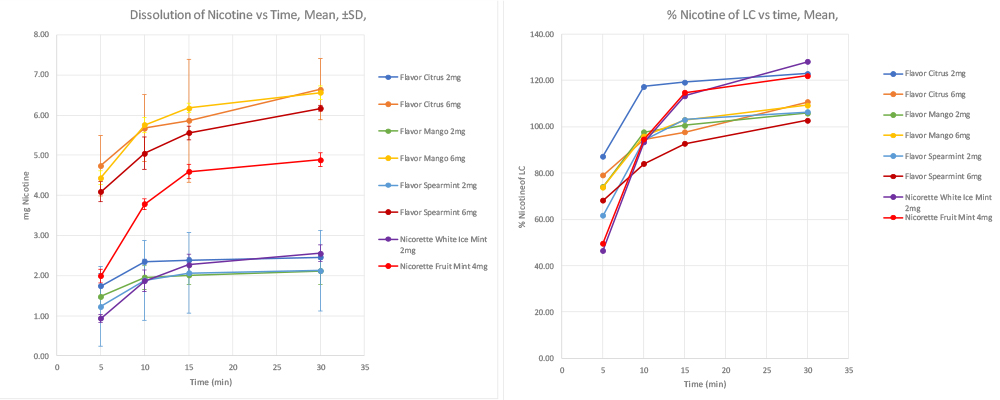
The chewing gum dissolution equipment is meant to simulate the chewing of a human jaw. The medicated gums are placed in a phosphate buffer or simulated saliva that is heated to 37 C. A piston masticates the gum in the buffer by pressing it and exerting a shearing force at its bottom position. Different total chewing time, chewing frequency and shearing angle can be used. At certain time-points, samples of the buffer with the dissolved or partly dissolved active ingredient from the chewing gum, are taken out for quantification. Conventional analytical techniques such as HPLC will yield the amount of substance that has been dissolved during the chewing process. We recommend the client let us also run a couple of well known gums on the market in the study as a reference.
A comprehensive and conclusive analytical report is provided at the end of the study.
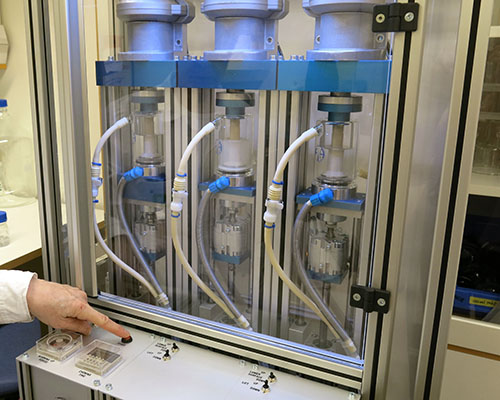

Rheological Testing of Medicated Chewing Gums
In addition to the well-known dissolution profile curves (amount vs time) we also offer measurement of the rheological properties of the chewing gum during the dissolution testing. These measurements are possible because of two built-in sensors; one sensor is measuring the force to press together the “jaws” and the other sensor is measuring the torque forces when the “jaws” are shearing the gum. These rheological data can be used as a useful fingerprint and indication of the “chewing feeling” of a gum, whether it is perceived by the consumer as soft and wet or as hard and compact. This information is an Important Input to formulators so that the desired chewing feeling for the consumer can be achieved.
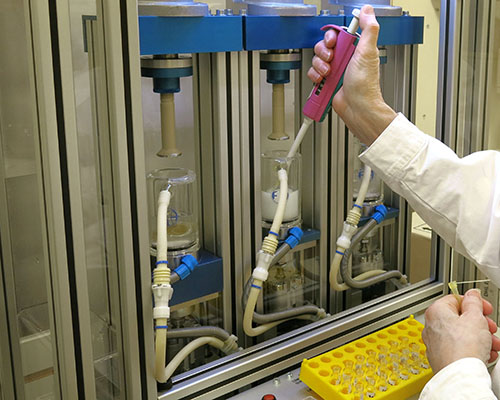





References
- L.C. Kvist, S. B. Andersson, S. Fors, B. Wennergren, J. Berglund, Apparatus for studying in vitro drug release from medicated chewing gums, International Journal of Pharmaceutics 189 (1999) 57-65
- L. C. Kvist, S. B. Andersson, J. Berglund, B. Wennergren, S. M. Fors, Equipment for drug release testing of medicated chewing gums, Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 22 (2000) 405-411
- L. C. Kvist, S. B. Andersson, J. Berglund, B. Wennergren, S. M. Fors, Equipment for Drug Release Testing Medicated Chewing Gums, Poster presented at the Tenth International Symposium on Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, May 1999, Washington DC, USA
